What is Web 3.0: Everything You Need to Know

It takes power from big tech companies, decentralizes it, and hands it over to individual users. We are talking about one of the most trending internet revolutions — Web 3.0.
Even if you aren’t up-to-date with the recent technology updates, you might have heard the term Web 3.0 often thrown around. But what exactly is Web 3.0, and how does it affect your internet experience? Let’s find out today.
What is Web 3.0?

Simply put, Web 3.0 is a new generation of the internet. Here, internet elements like websites and applications would be able to process human input in a much more human-like way.
For now, the internet can only understand the information it is fed on a conceptual level. However, a crucial part of human communication lies in the context that machines and the internet presently cannot comprehend. The upcoming internet generation aims to bridge this gap and create a seamless flow of communication between users and the internet.
With new technologies like big data, virtual reality, augmented reality, metaverse, machine learning, and decentralized ledger technology (DLT), information processing by the internet would be much more human-like.
The concept of Web 3.0 was first recognized by the inventor of the World Wide Web, Tim Berners-Lee. Initially called semantic web, the purpose of this new generation web was to be more independent, open-source, and intelligent.
Another revolutionary step taken for the development of Web 3.0 is the decentralization of power. Instead of storing data under a centralized entity and vesting the power in tech giants like YouTube, Netflix, or Google, information would now be processed and transferred in a decentralized way.
Rise of Web 3.0
W comprehensive understanding of a whole new generation of the Internet demands that we understand where exactly web generations come from. So, let’s start from the beginning:
Web 1.0
The initial years of the internet saw the era of Web 1.0. Although it wasn’t officially called so until recently, it depicted the most basic version of the internet. Websites in this era mostly had a static user experience.
This was also the time that saw the boom of industries like eCommerce. It was the same era where the first job boards monster.com and Hot Jobs and online auction sites like eBay were introduced to the world.
Web 2.0
After basic websites and static web pages came the era of web 2.0, which saw drastic personalization and interconnectivity.
On the user front, web 2.0 internet was much more accessible than web 1.0. Instead of reserving the ability to create and publish online content only to tech companies, web 2.0 encouraged the growth of user-generated content with social media platforms like Facebook and video publishing platforms like YouTube. Content creators could upload and share their content on a much wider level.
From a static, one-way communication model, web 2.0 transformed the internet into a communicative and interactive design.
On a technological level, web 2.0 made internet elements like websites and applications much more user-specific. Also, uploading content on websites became a breeze and autonomous; you no longer had to wait and refresh a page to see recent updates.
Key Features of Web 3.0
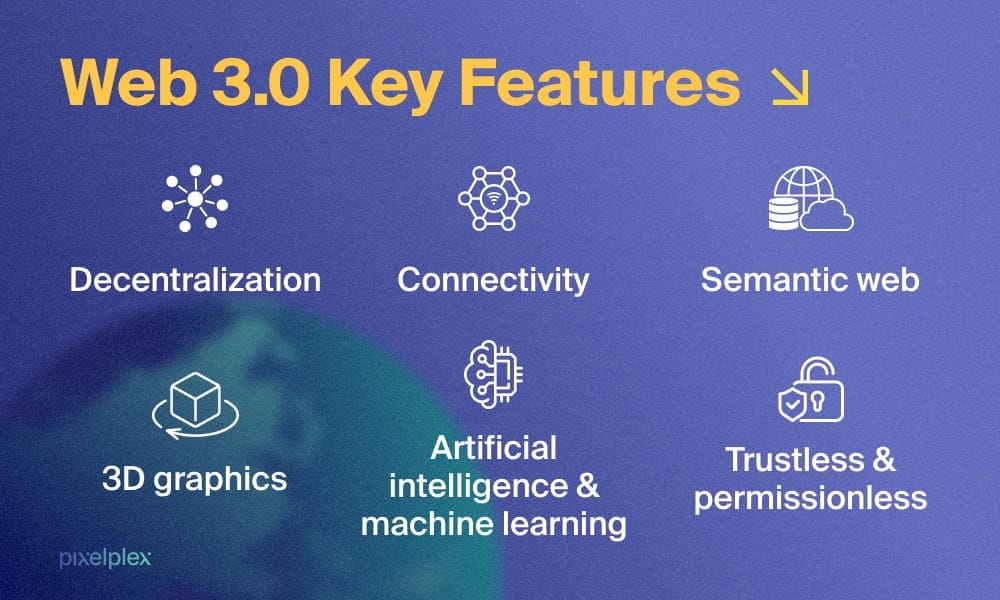
Here is what sets web 3.0 apart from all the earlier web versions:
1. Ubiquity
Ubiquity refers to the ability to be present everywhere at the same time. While web 2.0 has already offered a level of ubiquity with social networks allowing you to reach out to the world in just one click, web 3.0 has taken it a step forward. Instead of limiting the internet to mobiles and desktops, web 3.0 is coming up with several smart devices to make the internet a part of all your everyday tasks.
2. Semantic Web
The semantic web will help internet-powered devices to understand the context and emotion intertwined with a certain statement. For example, if you are using a voice typing system, it will recognize the emotion in your voice to use appropriate punctuation. If you want to type “Are you okay” as a question, the semantic web will recognize the tone in your voice and automatically insert a question mark.
3. Artificial Intelligence
To get to the bottom of human communication and its meaning, we need intelligent machines that understand every emotion, context, symbol, and expression just like a human does, and that’s where AI steps in. For example, by evaluating millions of internet user data, behavior, and searches, Google’s artificial intelligence bots can recognize and remove fake reviews to maintain the authenticity of online content.
4. Spatial Web
Web 3.0 will not limit your internet experience to 2D screens. In fact, its applications will be widely available in spatial, 3D models. The revolution has already begun with smart devices like TVs and voice assistants, which are 3D, tangible, and web 3.0 powered.
Web 2.0 vs Web 3.0 – What is the Difference?

Both these web versions have many noticeable similarities. For instance, both web 2.0 and web 3.0 have a user-centric approach with a focus on data personalization. Despite this, each of these generations is miles apart in terms of their other core features.
Let’s take a look into some of the most prominent differences between web 2.0 and web 3.0:
1. Approach
Web 2.0 thrived on the principles of interaction and personalization. It aims to turn static websites with absolutely no personal touch into dynamic web pages that cater to your specific needs and allow you to be a part of the process.
That’s why under web 2.0, we have applications like Facebook and Twitter that allow you to contribute to the internet and reach out to other users globally.
Web 3.0, on the other hand, focuses mostly on bridging the gap between human and machine communication. It focuses on decentralized internet authority and encourages machine learning so that search engines and internet algorithms can better understand the subtext and context of human communication.
Under web 3.0, we have voice assistants that convert verbal commands into comprehendible machine input to perform the desired action.
2. Application
The application of web 2.0 was only limited to the internet. You get to see it on website applications and other forms of web platforms but never through a tangible product. Web 2.0 gave us applications like Gmail and Netflix that we can only use within its own network.
However, web 3.0 focuses on creating tangible smart applications and offers higher individual user control. For example, voice assistant systems like Alexa and speech-operated applications like Smart TVs can effectively function in the user’s chosen environment without any third-party authority governing its usage.
3. Technology
Since the applications of web 2.0 are limited to websites, online platforms, and apps, its core technology only consists of coding languages like Java, HTML5, CSS3, AJAX, etc.
However, Web 3.0 has stepped out of device screens and requires advanced technologies like machine learning, artificial intelligence, decentralization, and big data.
While the technology of web 2.0 creates an interactive platform, the technologies used in web 3.0 make the platform’s interaction capacity human-like.
4. Data Ownership
The most revolutionizing move that came with web 3.0 was the shift in power over internet data and its usage.
Under the web 2.0 version, all the data was undisputedly owned by the network. Web users hardly had any choice in deciding how their data was used and shared. For example, when you create an account on Instagram, your personal information and preferences are stored, which are later used to curate personalized ads for you.
However, with web 3.0, you are the sole owner of your data, and you can control how it is used online. Every piece of information you share under web 3.0 is encrypted and often comes with a private key that only you have access to.
Top 4 Web 3.0 Examples
Although we have a long way to go before, we can completely adopt web 3.0 into our daily internet usage and activity, web 3.0 is surely no longer a talk of the future. There are quite a few web 3.0 applications that are currently storming the market and are widely loved by many. Let’s take a look at some of them.
1. Siri & Alexa
The most popular web 3.0 applications have to be Siri and Alexa. These voice-controlled personal assistants powered by Apple and Amazon use speech recognition technology to understand commands from the user and convert it into tangible action.
Since they’re directly using human speech recognition, they naturally understand the underlying context of every verbal command. Powered by AI and machine learning, Siri and Alexa also understand many international and regional languages.
2. Storj
The biggest benefit of Web 3.0 is data security. In a centralized system like web 2.0, the platform provider will own your sensitive data. However, web 3.0 and its decentralized approach give you all the authority over your personal data and files.
That’s the technology that Storj works on. Although some of its basic functionalities might match with cloud storage, it comes with added benefits like end-to-end encryption, private key authorization, and self-destructible data, where you can assign an expiry date to sensitive information.
To make these benefits widely available to the public, popular storage solutions like Comcast and Dropbox have already partnered with Storj.
3. Sapien
Sapien is the first decentralized social network that allows you to create your own applications on a blockchain-based platform. They will equip you with all the necessary tools you will need to create your own application through Ethereum blockchains which can be further used to organize your online activity through self-governing tools.
Each application created on this platform would be decentralized by default and capable of sharing information, communication, and transaction without making the users pay or post ads.
4. Wolfram Alpha
Wolfram Alpha is an intelligent platform that allows you to find solutions to questions. It is highly popular among students and professionals from academic backgrounds. Whether you have basic questions like the calorie content in a food or complex mathematical problems, Wolfram Alpha has an answer for everything.
Once you input your question, it will strive to thoroughly understand your requirements even on a contextual level, and provide you with an appropriate answer. The best part is that this application is instant and 100% accurate.
Do you need long-format answers to your question? Wolfram Alpha can help! For example, say you search “climate of New York.” In that case, it will give you a detailed insight into the fluctuating climate of the city, along with potential changes and a few facts that you can use to dive deeper into your research.
Drawbacks of Web 3.0
Presently the biggest concern as far as web 3.0 applications are concerned is the viability of this idea. Although data security and ownership features remain convincing, people are concerned about decentralized apps.
It is believed that despite all its decentralization and individual authority claims, most of the control would still be vested in venture capitalists and early adopters.
For example, the co-founder of Ethereum, Vitalik Buterin, who set out to create a decentralized network himself holds a lot of power and influence over Ethereum even though he is not a part of the development process anymore.
The same goes for other blockchain technology, and web 3.0-enabled platforms. On the surface, these are decentralized networks, but at the core, they are largely influenced by their respective founders, investors, and early adopters.
Bottom Line
Web 3.0 has slowly started to make its way into our lives. However, before we adopt it completely into our web networks, it’s best to investigate what you might be getting yourself into. Regardless of all the criticism it receives, web 3.0 certainly has a lot of potential to transform internet communication in every form. The only question is how realistic its ideas are, and that is something only time can tell.


